Help
This page is the user guide to IDD web server (http://dyn.life.nthu.edu.tw/IDD/IDD.php).
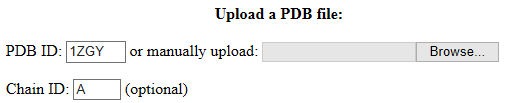
1. In the webserver, you can either enter the PDB ID and chain identifier (Chain ID) of the protein or manually upload a PDB file.
2. To calculate intrinsic dynamics domains (IDDs)
a. for a single structure, you can choose one of the two elastic network (EN) models or the geometry based method (referred as PC1 based method in the publication). The EN model can either be Gaussian network model (GNM (Bahar, Atilgan, & Erman, 1997)) or anisotropic network model (ANM, (Atilgan et al., 2001)).
b. for multiple structures, please choose the principal component analysis (PCA (Yang, Eyal, Bahar, & Kitao, 2009)) based method.

3. If an email address is provided, the link to the results will be e-mailed (optional).
![]()
4. Press Submit and Run IDDs to submit the job.
5. When the calculations are completed, you will automatically be redirected to the results page.
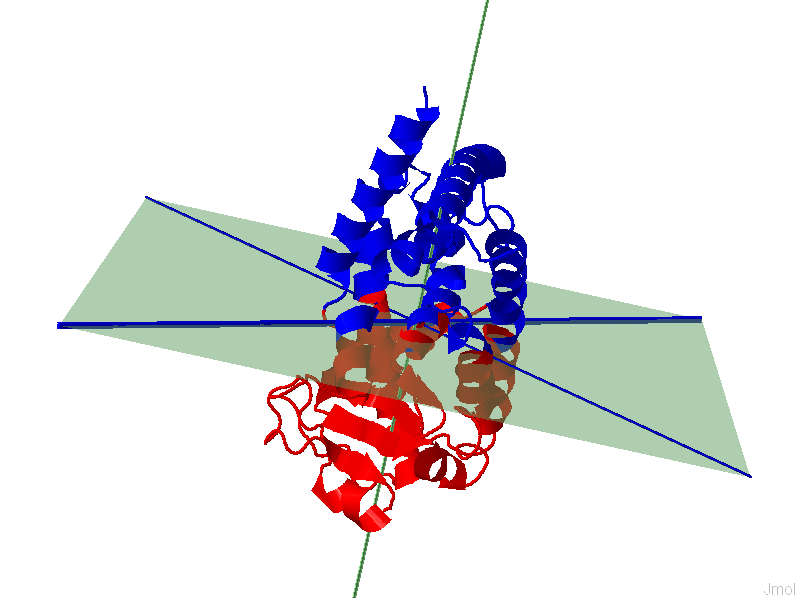
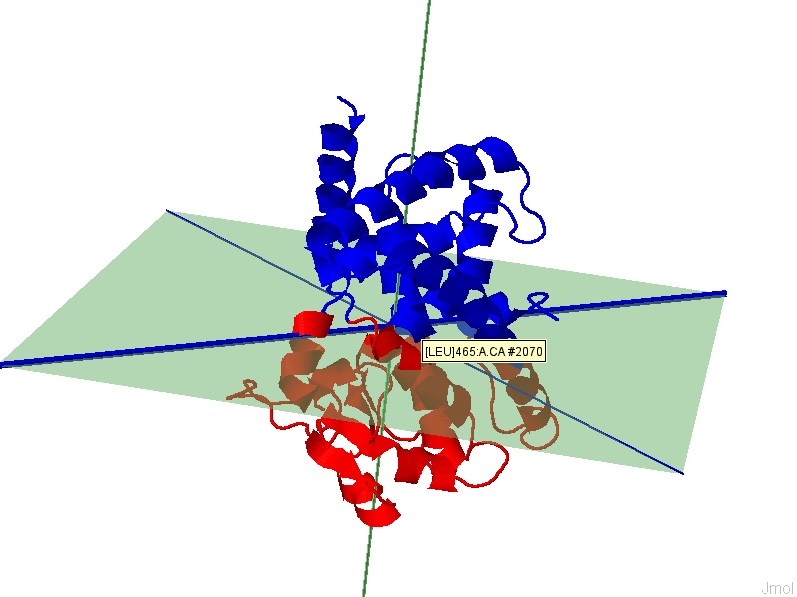
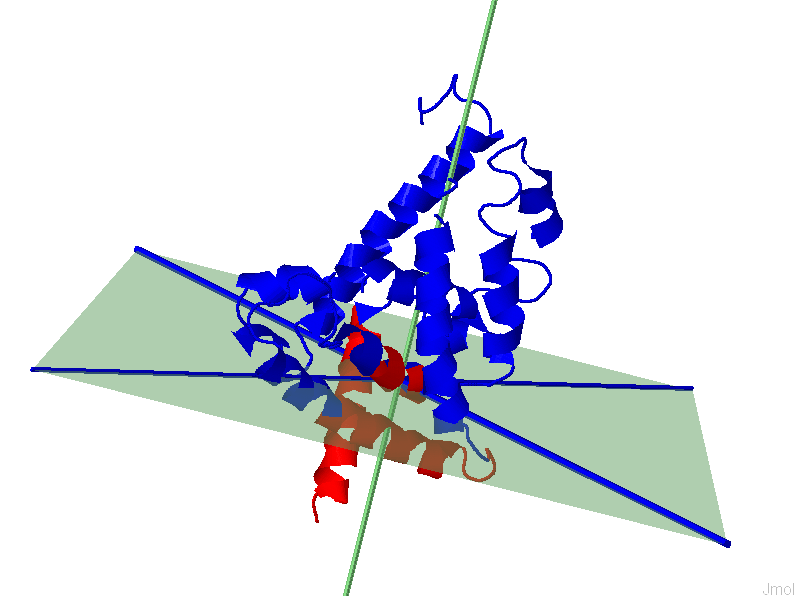
i. The results page will display a 3D representation of the molecule using JMol. Residues of the same dynamics domains are colored in either red/blue. The domain plane (D-plane) or splitting plane (S-plane) and the corresponding normal are colored in green. The thick blue axis on the plane represents domain axis (D-axis) or splitting axis (S-axis).
Note:
a. The results will be available in the server for a period of 30 days.
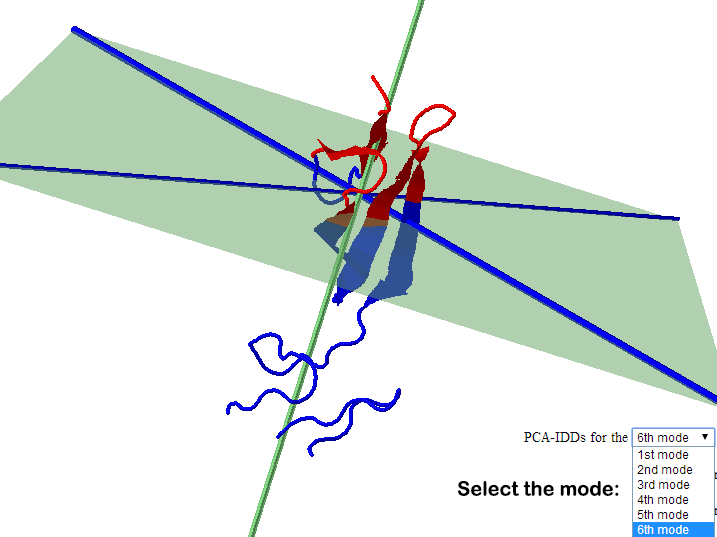
b. The user can choose to visualize IDDs from each of the first 6 modes in all cases except shape based IDD.
|
Part of the result page for shape based IDDs (left) and PCA based IDDs (right) |
|
|
PDB 1ZGY , Chain A
|
PDB 2CKU , Chain A
|
ii. Details of the IDD calculation are also shown. The position (mean position of transition points) of D-plane/S-plane, plane normal and D-axis/S-axis is shown. Also shown is the direction of the plane normal and D-axis/ S-axis (domain axis). Higher F(n) value suggests better separation of intrinsic dynamics domains. One can appreciate the implication of separation quality by viewing the figure below. The results for the 1st (left, F(n)=2.73)) and 6th (right, F(n)=0.09) modes of GNM based IDD calculations are shown for protein 2F0R, Chain A. One can notice that a higher F(n) values gives a clearer separation between Res+/Res- residues.
|
GNM, 1st mode, F(n)=2.72
|
GNM, 6th mode, F(n)=0.09
|
All the output files can be downloaded as a tar file. The following details can be found in output*.txt in the tar file. The *.vmd file helps user to visualize the results using VMD program.

iii. Downloadable files (also found in *.tar file). 5 files for each mode.
|
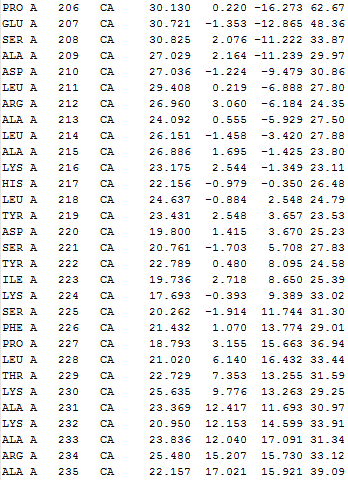
(1) 3D structure of color-coded IDDs |
PDB |
|
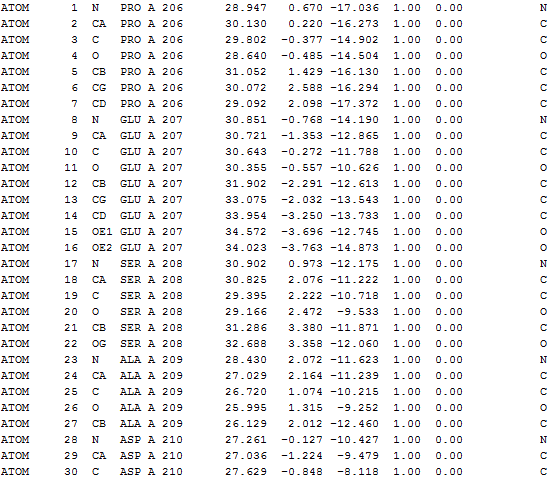
(2) 3D structure of color-coded Res+/Res- (except in shape based IDD) |
PDB |
|
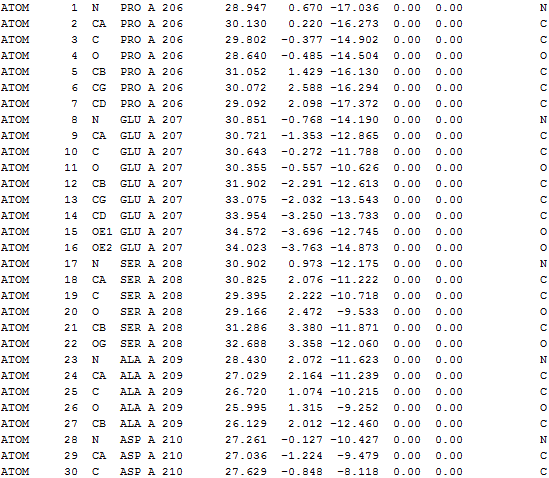
(3) Nodes taken for IDD calculation |
PDB |
|
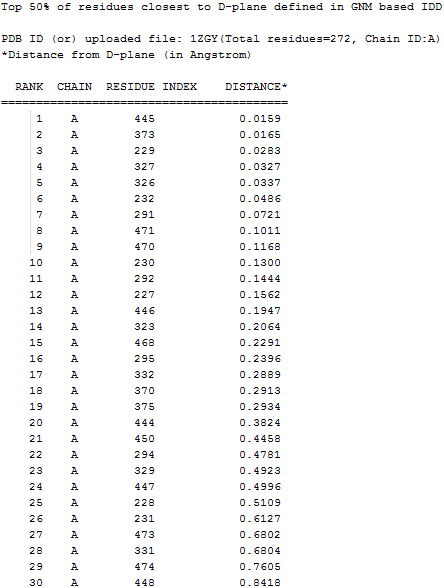
(4) Top 50% residues with the CA atoms are closest to the D-plane/ S-plane |
TXT |
|
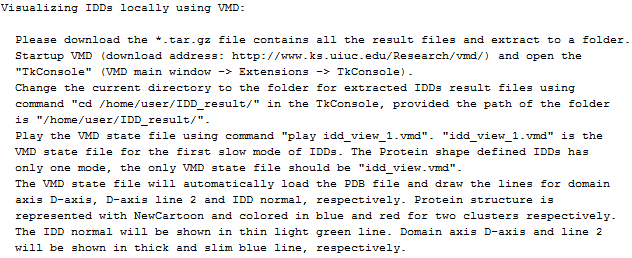
(5) Further information (e.g. visualizing IDDs locally using VMD) |
TXT |
Sample files for each of the results are shown below (PDB: 2CKU, Chain A)
|
3D structure of color-coded IDDs
|
3D structure of color-coded Res+/Res-
|
|
Nodes taken for IDD calculation (only Cα atoms)
|
Top 50% residues with the CA atoms are closest to the D-plane/ S-plane
|
|
Further information
|
|
6. JMol and browser plugins
The Results page uses JMol to visualize results which relies on Java Virtual Machine. We suggest users to install Version 7 Update 55 (released in April, 2014) or higher. When the Results page is loaded, the JMol applet is automatically started and you will be prompted with a request from your browser asking if you want to allow it to run. If Java is not already installed on your computer, please download and install it; if not, Java can be obtained from the Java site. More details on JMol can be found from the JMol site.
Reference:
Atilgan, a R., Durell, S. R., Jernigan, R. L., Demirel, M. C., Keskin, O., & Bahar, I. (2001). Anisotropy of fluctuation dynamics of proteins with an elastic network model. Biophysical Journal, 80(1), 505–15. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76033-X
Bahar, I., Atilgan, a R., & Erman, B. (1997). Direct evaluation of thermal fluctuations in proteins using a single-parameter harmonic potential. Folding & Design, 2(3), 173–81. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9218955
Yang, L.-W., Eyal, E., Bahar, I., & Kitao, A. (2009). Principal component analysis of native ensembles of biomolecular structures (PCA_NEST): insights into functional dynamics. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 25(5), 606–14. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp023